The world focuses more on gut health in this day and age, when everyone is becoming health-conscious. Fermented foods are one of the best tools for maintaining proper gut health. Fermented foods impressively spice up the taste in flavor while providing multiple health benefits that can really transform one’s health. From kimchi to kombucha, the wide variety of fermented foods available today provides delicious options to support gut health, improve digestion and maintain a balanced gut microbiome. Henceforth, let’s take a bit of a dive into the realm of fermented foods and bring to light its benefits.
What are the Health Benefits of Fermented Foods?
How do Fermented Foods Improve Gut Health?
Beneficial by nature, fermented foods seek to improve one’s gut health due to the presence of probiotic bacteria. Fermentation encourages the production and growth of beneficial microorganisms, enhancing the number of good bacteria within the intestines. Hence, a well-balanced gut microbiota is important for optimal digestion and absorption of nutrients, as well as immunological response. Fermented foods benefit gut microbiota by encouraging the growth of beneficial bacteria, thus enhancing an individual’s digestive health. According to research, a healthy gut microbiota did cut the risk of digestive disorders and even risk factors associated with diseases such as type 2 diabetes. The benefits of fermented foods go beyond digestion; these foods help to enhance the immune system and even promote mental health by the influence of what is called the gut-brain connection.
What Nutrients are Found in Fermented Foods?
Fermented Foods contain a multitude of nutrients that aid in maintaining optimal health. These foods are rich in vitamins, specifically the B vitamins, which have a special role in energy metabolism. Fermented milk such as yogurt and kefir is perhaps the best-known source of calcium and protein, necessary for good bone health. Check out the fermented vegetables: sauerkraut is one of the best sources of fiber, which is excellent for digestion and prevents shapes of constipation. Besides this, fermentation promotes the bioavailability of certain nutrients, which helps in easier absorption of such nutrients by our body. It means by consuming fermented foods we can take better amounts of vitamins and minerals, bringing improved overall health.
Can Fermented Foods Aid Digestion?
Fermented foods are really great for digestion due to their high probiotic content. Probiotics help digest food more efficiently, relieving issues such as bloating and constipation. Beneficial bacteria found in fermented foods do work in tandem to create balanced gut conditions that are essential for proper digestion. In addition to that, due to the formation of organic acids as a result of the fermentation process, regulating the acidity of the stomach is made easier for food digestion. Some people, for example, will easily digest yogurt and kefir, which are fermented dairy products because lactose in those products has been broken down through fermentation, therefore making those products a better option for them.

Which Popular Fermented Foods Should You Include in Your Diet?
What is Kimchi and How Does it Benefit Gut Health?
Kimchi, a traditional Korean dish based on fermented vegetables, usually cabbage, packs a gastrointestinal wallop. Fermented foods like this one are rich in lactic acid bacteria that can help improve the gut microbiome and gut health in general. The fermentation process gives longevity to the vegetables and also adds beneficial compounds that can strengthen the immune system and help with the inflammation process. Continuous intake of kimchi can help balance gut flora, improve gut health, and enhance well-being.
Why is Yogurt Considered a Probiotic Food?
Yogurt is often considered one of the best sources of probiotics. An equally beneficial fermentation process brought to yogurt by the addition of specific strains of bacteria-Lactobacillus and Streptococcus-is responsible for the fermentation of milk into yogurt. These probiotic strains function to restore and maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria, thus promoting better digestion and nutrient absorption. In addition to those qualities, yogurt also delivers a potent dose of protein, calcium, and B vitamins, thus proving to be a substantial contribution to any diet. One can take yogurt plain, put it in smoothies, or use some as a base for dressings; yogurt is indeed another versatile fermented food that provides many other benefits for health.
What are the Benefits of Drinking Kombucha?
Kombucha, a fermented tea, has ever-increasing popularity because of its tantalizing flavor and health benefits. This sparkling drink is produced from brewing tea and sugar with bacteria and yeast; the beverage is abundant in probiotics. The benefits of drinking kombucha include the balancing of the gut microbiome and aiding in food digestion, hence supporting digestive health. Moreover, they contain organic acids and minerals that might promote liver function and proper cholesterol levels. Incorporating kombucha into diet is a delicious way to achieve gut health while treating oneself to an exquisite, bubbly drink.
How to Incorporate Fermented Foods into Your Diet?
What are Some Easy Fermented Foods Recipes?
It is easy to incorporate fermented foods into the diet, and the process can be enjoyable if he starts with a couple of easy recipes requiring just a few ingredients and minimal effort. An illustration of this would be a humble dish of fermented vegetables-cabbage chopped with salt and set aside to ferment at room temperature for some days. It’s a basic sauerkraut recipe that will certainly add joy to any salad, sandwich, or dish that’s eaten as a side. Another simple recipe is yogurt with fruits and honey-perfect for a nutritious and very tasty breakfast or snack. These straightforward methods will be a swift and easy introduction into the world of fermented foods.

How Can You Make Your Own Sauerkraut?
Making sauerkraut from home is a fulfilling and satisfying experience to put you in charge when it comes to gut health. All you need is a head of cabbage and some salt. Shred the cabbage, place it in a large bowl, and mix well with salt. It’s going to be salt that extracts water from the cabbage and produces brine. A clean glass jar is then tightly packed with cabbage so that it is submerged, in its own liquid again, in some height. It’s all covered with a cloth, and it should sit at least a week or up to four, depending upon how sour you want it to be. Once fermented, it becomes a relish or side on its own or a main topping for a variety of dishes.
What are the Best Ways to Use Miso in Cooking?
Miso, the fermented soybean paste, is a highly adaptable ingredient that can impart both flavor and nutrition to your meals. One of the most efficient ways to add miso to your life is by using it as a base for soups: just dissolve in hot water a spoonful of miso and throw some veggies and tofu-this is a healthy and warm dish. Miso can also be combined into a marinade for meats or vegetables; you’re getting tons of umami flavor while contributing helpful bacteria. It can even be mixed into dressings or sauces to add that much-needed complexity and depth-a great way to enjoy all the health benefits that fermented foods have to offer.
What is the Role of Microorganisms in Fermentation?
What Types of Bacteria are Found in Fermented Foods?
In fermentation, microorganisms are mostly used, such as bacteria and yeast, to convert food into their fermented delicacies. Lactic acid bacteria, among them, such as Lactobacillus and Leuconostoc, are implicated in those fermented foods as sources of tangy tastes and probiotic goods in the foods. These bacteria ferment sugars into lactic acid; this increases foods’ shelf life and improves nutritional value. And besides, the beneficial bacteria help with gut health because they create a balanced gut microbiota necessary for proper digestion and immune function.
How Do Yeast and Bacteria Work Together in Fermentation?
During the fermentation process, yeast and bacteria work symbiotically together to create complex flavors and health benefits that are additive to fermented foods. In many cases, yeast, such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae, may ferment sugars into alcohol and carbon dioxide, while bacteria convert sugars to organic acids, presenting the sour taste in products like yogurt and kombucha. This collaborative fermentation process elicits a spectrum of flavors and a range of probiotic functions, ushering in health benefits in fermented foods. The interactions between yeast and bacteria form one of the most interesting paradigms of fermentation, improving not only the flavor of foods but also their health-promoting properties.
What is the Gut Microbiome and Its Relation to Fermented Foods?
The gut microbiome refers to the immense community of microorganisms that populate the gastrointestinal tract, and it is crucial to digestive process, immune function, and overall health. Fermented foods can exert a tremendous influence on the gut microbiome by introducing good bacteria needed for balancing an ecosystem. A varied and numerous range of fermented foods results in a more diverse microbiota, which correlates with better health outcomes. It has also been suggested that a healthy gut microbiome can behave as a protective shield against diseases such as obesity, diabetes, and inflammatory conditions. Thus, including different fermented foods in your diet could serve as a potential strategy for facilitating a champion microbiome.
Can Fermented Foods Help with Digestive Health Issues?
How Do Fermented Foods Affect Cholesterol Levels?
There are studies which indicate that fermented foods in a daily diet can boost the health of cholesterol levels. Probiotics in these fermented foods might, perhaps, aid in reducing total cholesterol and LDL (bad cholesterol) while increasing HDL (good cholesterol). Since probiotics may enhance the gut health of an individual to facilitate the way fats are metabolized, they can help lower cholesterol levels. Adding fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and tempeh could be worth a shot for all those who are looking to naturally manage cholesterol.
What are the Effects of Fermented Foods on Digestive Disorders?
Fermented foods have shown potential in addressing different types of digestive disorders such as IBS or IBD. The probiotics in these foods can boost the gut microbiota’s balance, minimizing various symptoms such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea. The fermentation process also increases the digestibility of certain foods, making them less harmful to the stomach. People suffering from digestive disorders may seek relief through the use of fermented foods within their diets and thus create a gut environment that promotes health.
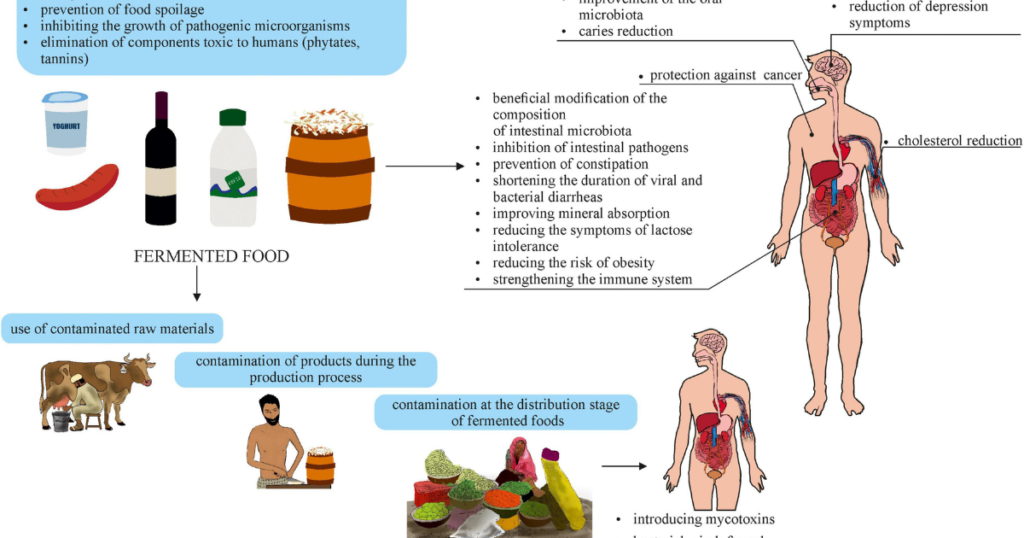
Are There Any Risks Associated with Eating Fermented Foods?
While fermented foods offer many health advantages, they should be consumed with caution. Some individuals may experience mild digestive discomfort when these foods are first added to their diet, especially when not accustomed to consuming probiotics. It is usually wise to begin with small amounts and increase dosage over time. People with specific health issues, such as histamine intolerance or allergies to certain fermented foods, should seek professional medical advice before making drastic changes in their substituted foods of choice. All in all, fermented items can be added into your daily meals if taken with ease; the dishes are just delicious and healthy too.
FAQs
Q: What are fermented foods and how do they benefit gut health?
A: Fermented foods are products that have undergone the process of fermentation, where microorganisms like bacteria and yeast break down sugars. They benefit gut health by introducing probiotics, which help maintain a balanced microbiome and improve digestion.
Q: What is kefir, and how can I incorporate it into my diet?
A: Kefir is a fermented drink made from kefir grains that contain a mix of bacteria and yeast. You can incorporate it into your diet by using it in smoothies, salad dressings, or simply drinking it on its own.
Q: Can you explain the difference between fermented dairy foods and plant-based fermented foods?
A: Fermented dairy foods, like kefir and yogurt, are made from milk and contain probiotics beneficial for gut health. Plant-based fermented foods, such as tempeh and fermented kimchi, are made from plant foods and provide a different range of nutrients and probiotics.
Q: How does the intake of fermented foods impact overall health?
A: The intake of fermented foods can enhance digestion, boost the immune system, and improve gut health by providing a rich source of probiotics and aiding in food preservation.
Q: What are some popular recipes to try using fermented foods?
A: Some popular recipes include smoothies with kefir, salads topped with fresh or fermented kimchi, and dishes using tempeh as a protein source. You can also try making your own kombucha, a fermented tea.
Q: How does apple cider vinegar fit into the category of fermented foods?
A: Apple cider vinegar is a fermented drink made from apples through a fermentation process that includes both alcoholic fermentation and acetic acid fermentation, making it beneficial for digestion and gut health.
Q: What role do microorganisms in fermented foods play in gut health?
A: Microorganisms in fermented foods, such as probiotics, help balance the gut microbiome, improve digestive health, and may enhance the absorption of nutrients from other foods in your diet.
Q: Is kombucha a good option for improving gut health?
A: Yes, kombucha is a fermented tea that contains probiotics which can help support gut health and improve digestion. However, it’s essential to consume it in moderation due to its acidity and sugar content.
Q: How can I start incorporating more fermented foods in food guides into my daily meals?
A: To incorporate more fermented foods into your meals, you can start by adding items like yogurt, kefir, tempeh, and fermented kimchi to your grocery list and exploring different recipes that highlight these ingredients.


