Millennials, the contemporary adult generation born between 1981 and 1996, have been one of the most remarkable agents of contemporary society. Millennials will remain the biggest generational group in the labor force, pushing over a million millennials to serve as the generation that shall be behind all the internal diversity of the potential output by its various parts (consumer’s behaviour, office’s behaviour, etc. This article will delve into the key characteristics of millennials, explore the impact of the Great Recession on their lives, analyze their relationship with Generation Z, examine the role of the internet in their upbringing, and assess how they are influencing society today.
What are the Key Characteristics of Millennials?
Millennial Age Range and Birth Years
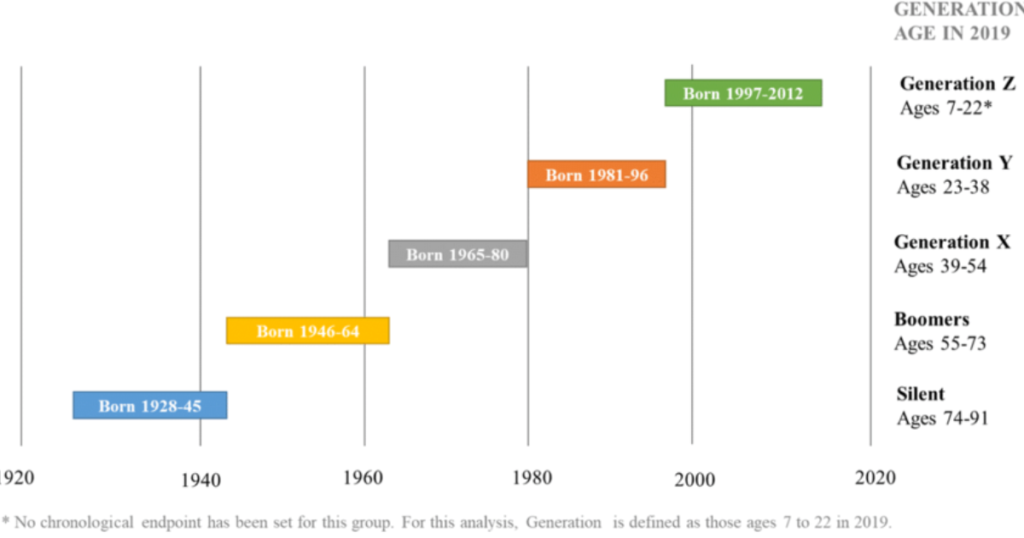
The millennial generation, also referred to as the millennial generation, includes individuals having birth years between 1981 and 1996. The characteristic that differentiates this generation from previous ones like Generation X (born between 1965 and 1980) or baby boomer (born between 1946 and 1964) is this. Millennials oldest now in their 40’s, this generation is heterogeneous, a mixture of people who all faced deep social change. This population is defined as a link between the traditionalists of the silent generation and the ascendant Generation Z (late 1990s to early 2010s) by Pew Research Center. In order to properly place their own experience and problems in modern society, understanding the millennial age span is extremely important.
Millennial Values and Beliefs
Millennials’ values and beliefs are drastically different than those of the previous generations, the older generation. Many millennials prioritize social justice, environmental sustainability, and inclusivity, reflecting a collective consciousness that is often seen as more progressive than that of Generation X and the baby boomers. With this intergenerational change, cultures have changed at all levels, from the market, consumerism, politics, and employment. Digital born again millennials are skilled at using tech to promote ideas and are thus a culture of openness on transparency and accountability. This development in values molds the way millennials relate with the society and how the institutions they expect from are.
How Millennials Compare to Generation X
Comparing millennials with Generation X, important contrasts appear in the lifestyle, work ethic, and attitude towards technology. Gen Xers, known for their independence and resourcefulness, grew up in a different socioeconomic fabric, that is especially important in their early life. Because of this, millennials have become users of technology and digital communication in a way that is quite different for their Gen X counterparts. Although Gen Xers tend to value the traditional stability and sequential trajectory of the career, the Millennials are genetically driven to maximize the degree of flexibility, work-life balance, and operate a business. This generational contrast illustrates the ongoing development of social norms and standards.
How Did the Great Recession Affect Millennials?
Millennials and Economic Challenges
Great Recession, at the turn of the 2000s, produced a profound legacy for the millennial generation. As many millennials came of age during this tumultuous time, they faced unprecedented economic challenges that shaped their life choices. The high unemployment rates and the crushing burden of student debt forced many millennials to delay traditional milestones such as homeownership and starting families. This economic reality generated a whole generation of individuals unwilling to achieve financial security and may highlight the subjective worth of life experience and working through their personal success over earthly assets.
Impact on Millennial Job Market and Careers
The bounce from the Great Recession dramatically changed the employment terrain for millennials. With many of the blue-collar traditional industries disappearing, millennials faced the challenge of working in the environment of gig work, freelance work, and career non-conformity. This trend has led to a workforce of “tough” workers, experts in technology and remote work. Conversely, the pressure to achieve a rewarding career has also generated a sense of uncertainty in millennials, and as a result, a reassessment of success on their terms. Hence, the attitudes of a pragmatic generation demanding not just economic security but also a sense in the work it performs are seen to be quite a lot.
Long-Term Effects on Millennial Financial Stability
Millennial financial resilience has been profoundly-affected, as a result of the Great Recession. Millennials on entering the labor market, owing in part to substantial student loan debts and low labor market prospects, have been unable to be savers and investors. This financial burden has resulted in a generation more cautious of risk than previous generations. Millennials are increasingly minded to build their financial security in their 30s and 40s, tending to place a premium on savings and investment rather than consumption. The burden of the Great Recession has put a fear of repercussions in millennials’ minds, thus affecting their financial life dramatically for years ahead.
What is the Relationship Between Millennials and Generation Z?
Defining Generation Z vs Millennials
With millennials continuing to mold the world, Generation Z has introduced yet another dimension to the nuclear generation model. Members of Generation Z, often referred to as Gen Zers, were born from the late 1990s to the early 2010s and have grown up in a world heavily influenced by technology. Whereas millennials, are sometimes referred to as digital natives, Gen Z are, in fact, pure digital citizens having grew up in an internet and social media world from a young age. This separation has led to peculiar dynamics between the two generations, above all in their behavior towards communication, activism and social problems.
Similarities and Differences in Values
Notwithstanding their diverging backgrounds, there are some resemblances in millennials and Gen Zers’ values. Across generations, they both embrace social justice, social inclusion and environmental activism, often using social media to address the socially relevant questions. Nevertheless, Gen Z´ers are with a pragmatic attitude and usually they give priority to practical solutions instead of it just being a pure and ideal dream. This generational aspect can be explained by the different social problems faced by each generation group, which, also highlights, the need to take into consideration these differences when confronting future societal trends.
How Both Generations Influence Each Other
Millennials and Gen Z bond (rather than only with influence but with collaboration). When older millennials interact with younger Gen Zers, learning from and with each other, the two generations share knowledge and insights gained from the one another. With this crossing over, there has also been a commitment to social change and activism building together, and it turns out to be very powerful to generate movements that resonate across generations. The hybridization of the minds and beliefs of millennials and Gen Zers is creating a new cultural discourse based on mobilization, which is now essential to understand, and to learn from, both generations of innovating advocates for social change working together.
How has the Internet revolution increased on their backs shaped Millennials?
Millennials as Digital Natives
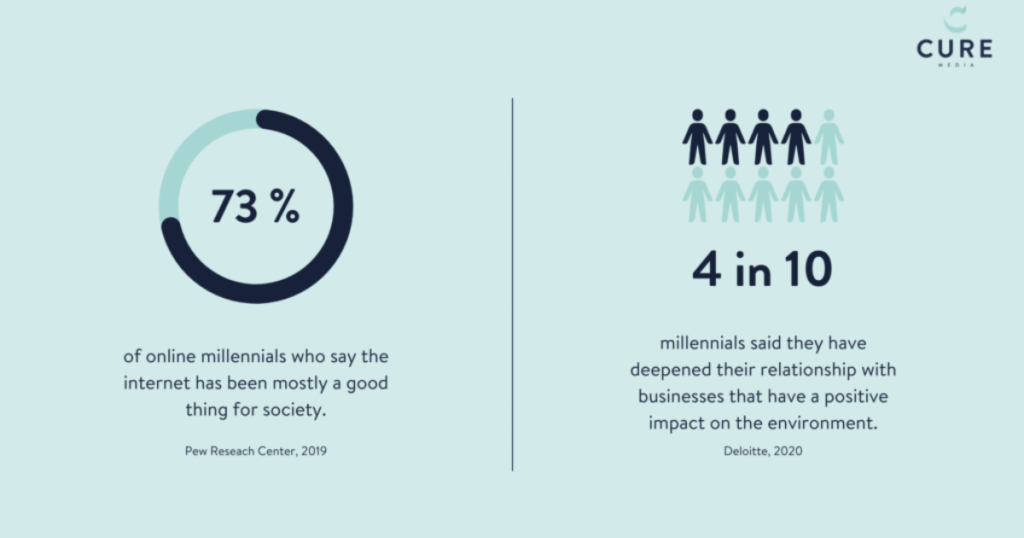
Millennials have been profoundly conditioned by the internet age, leading them to be the first generation raised with technology woven into the fabric of life. Being digital natives, the millennial generation has learnt to utilize the internet as an instrument for inter-personal communication, learning and self-expression. This bond with technology has affected their mode of social interaction, career paths, and consumption processes. Instantaneous access to information has equipped the millennials (class of living in the 20th Century or the 21st Century) to have the knowledge to know about things and then has equipped them to fight for the causes they are personally passionate about on internet platforms.
Social Media Influence on Millennial Culture
Social media has been a key driver in shaping millennial culture. Platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter have not only changed the way millennials communicate with each other, but also their consumption habits, and lifestyle. Social media use by millennial generation plays an important role in self-marketing and brand building, which is often mixed with personal and business identities. This special relationship with social media has created an atmosphere of authenticity and social engagement, which helps millennials to connect with the world via sharing a story.
The Internet’s Impact on Millennial Communication
The Internet has changed millennial communication for the better by enabling rapid communication over long spans. Millennials, in turn, tend to favour digital rather than conventional modes of face-to-face communication. This trend has consequences for the workplace, for personal relationships, and for community involvement. Through this dependence on technology, greater connectivity has come at the expense of concerns with whether interpersonal relationships are high quality, whether people may become isolated, etc. The meaning of this duality is very important in dealing with the issues of how the millennial generation is able to cope with its world of information.
How Are Millennials Impacting Society in 2024?
Millennials’ Influence on Consumer Trends
The millennial, as the largest workforce generation, will play a big role in consumer trends in 2024. Becoming consumers of sustainable, ethical and experiential products has changed the market, forcing brands to take notice of their expectations. Millennials are more likely to back companies that share their views, paying a premium to companies that promote transparency and social responsibility. This change in consumer behavior has resulted in growing demand of sustainable schemes and morally upright business structures, and has therefore forced companies to reassess methods to comply with this powerful segment of the population.
Millennials and Workplace Dynamics
Millennials are changing the work environment, demanding flexibility in work conditions, diversity and inclusion in the work environment. The focus on work-life balance and mental health has led organizations to establish more flexible work policies, leading to an environment where employees are respected and supported. With increased numbers of millennials entering positions of leadership, the impact on corporate culture will certainly result in further transformation, leading to a more integrated approach to employee wellbeing and organizational achievement.

Millennials Driving Social Change and Activism
Millennials will lead the way in 2024 social activism and social change as a cohort of concentrated power to catalyze immediate societal transformational change. Millennials are pushing the old way of doing things, and demanding accountability for the institutions that must weather the storm. Their desire to be participant and to act for the change development started a chain reaction, which is influencing now new generations. Maintaining their position of power to promote the common good (i.e., the common good of society), millennials not only reshape society but also redefine the concept of the citizen in the modern society.
FAQs
Q: What defines millennials and how do they differ from other generations like Gen Xers and Gen Z?
A: Millennials, also known as Generation Y, are typically defined as individuals born between 1981 and 1996. They differ from Gen Xers, who were born between 1965 and 1980, and members of Gen Z, who were born from the late 1990s to early 2010s. Each generation has unique characteristics shaped by the socio-economic context they grew up in.
Q: What are some key characteristics of millennials?
A: Millennial characteristics include a strong emphasis on technology, a preference for collaboration in the workplace, and a desire for meaningful work. They tend to value experiences over material possessions and are known for their adaptability to change.
Q: How do millennials value work-life balance compared to previous generations?
A: Millennials value work-life balance significantly more than previous generations, such as the Greatest Generation and Gen Xers. They often seek jobs that offer flexibility, remote work options, and a supportive work culture that prioritizes well-being.
Q: What impact have millennials had on the workplace?
A: Millennials in the workplace have transformed corporate culture by advocating for diversity, inclusion, and a focus on mental health. They tend to prefer collaborative environments and often challenge traditional hierarchical structures in favor of more egalitarian approaches.
Q: How do millennials in the United States differ from millennials in the West?
A: While millennials in the United States often face unique economic challenges, such as student debt and housing affordability, millennials in the West may experience different cultural expectations and social norms that influence their values and lifestyle choices.
Q: What are some common misconceptions about millennials?
A: Common misconceptions about millennials include the belief that they are entitled or lazy. In reality, many millennials face significant economic challenges and are often more pragmatic than previous generations due to their experiences during economic recessions.
Q: What role do millennial women play in shaping societal trends?
A: Millennial women are significant drivers of change in various sectors, advocating for gender equality, sustainability, and social justice. Their values often influence consumer trends and workplace policies, leading to more inclusive practices in society.
Q: How do younger millennials differ from older millennials?
A: Younger millennials, typically those born in the mid to late 1990s, often have different perspectives shaped by the rise of social media and technology during their formative years. This contrasts with older millennials who witnessed the transition from analog to digital technology.
Q: What challenges do millennials face today?
A: Millennials face several challenges today, including economic instability, high levels of student debt, and the impact of global crises such as terrorist attacks and pandemics. These challenges shape their values and decision-making processes in both personal and professional realms.
Q: How do millennials view the future compared to previous generations?
A: Millennials tend to have a more optimistic yet realistic view of the future compared to previous generations. They are often more focused on social responsibility and environmental sustainability and are willing to advocate for change to create a better world for future generations, including Generation Alpha.




